Table of Contents
Many patients seek advice for joint pain and reflect on their concerns about arthritis. But do we know what arthritis is? What are the symptoms? Who does it affect? How do we improve the pain? Do we have to take medication?
Arthritis is a general term that refers to inflammation and stiffness of the joints. It is not a disease in itself.
This condition can manifest itself in a variety of ways and can affect people of all ages, races, and genders. From young athletes to the elderly, arthritis does not discriminate.
Osteoarthritis is the most common cause of arthritic joints, impacting around 10 percent of the general U.S. population.
Read on to learn more about this problem.
What is arthritis?
Arthritis refers to inflammation and stiffness of a joint. It is not a disease in itself. Arthritis is often divided into inflammatory and non-inflammatory types. It is a condition present in different diseases, including:
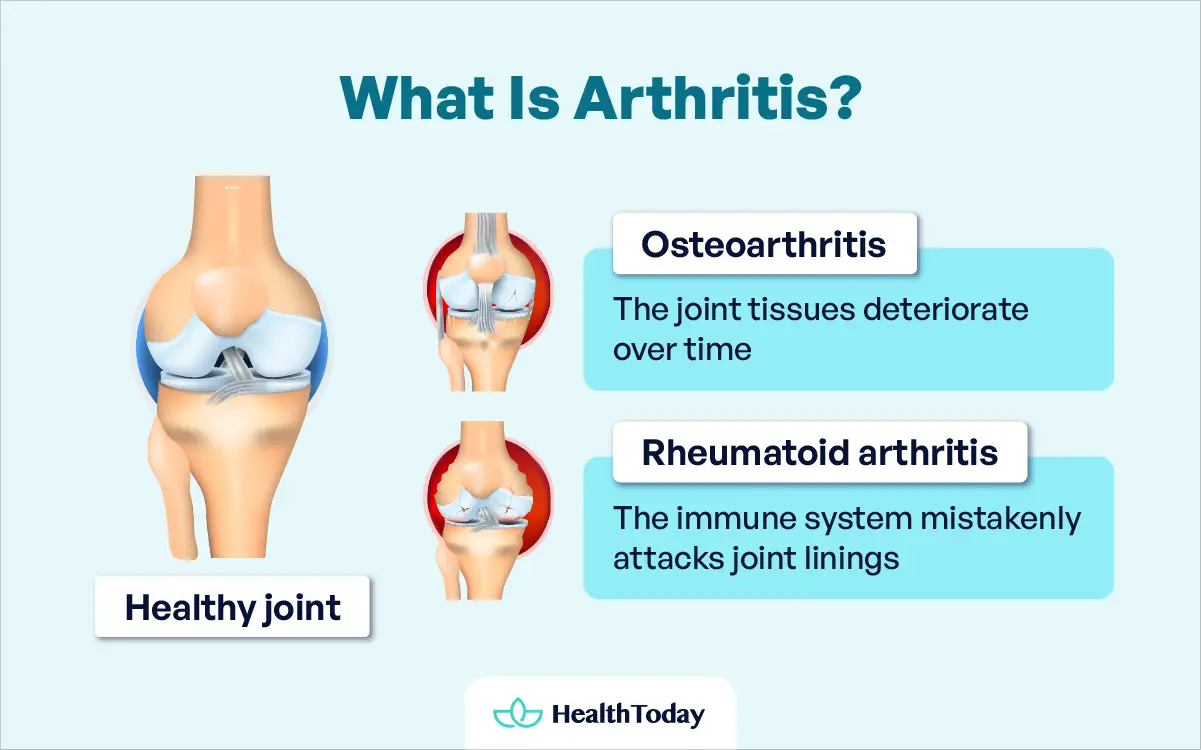
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that primarily affects the cartilage, the tissue that covers the ends of the bones in a joint. It is considered one of the most common forms of arthritis and is often associated with aging and normal joint wear and tear.
Inflammatory arthritis
Inflammatory arthritis is a group of diseases whose etiologies range from infections to autoimmune mechanisms in which the body attacks its own joints and tissues (1). Rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis are the two most common types of autoimmune inflammatory arthritis, although there are over 100 arthritis types.
Joints can become inflamed for multiple reasons. When people think of inflammatory arthritis, they often think of rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic autoimmune disease that predominantly affects the joints. It is the most common autoimmune inflammatory arthritis, affecting 0.5 to 1 percent of the general population (2).
In rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system mistakenly attacks the lining of the joints, causing inflammation, pain, swelling, and, eventually, joint damage.
The risk factors for developing rheumatoid arthritis are multiple, with the following standing out (3):
- Family History: People with a family history of rheumatoid arthritis have an increased risk of developing the disease. This indicates a genetic predisposition to RA.
- Sex: The incidence of RA is about three times higher in women than in men.
- Age: It usually develops between the ages of 30 and 50. However, it can also occur in children and older adults.
- Smoking: Cigarette smoking has been associated with an increased risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis, as well as increased severity of the disease in those who already have it.
- Environmental exposure: Exposure to certain environmental factors, such as viral or bacterial infections, can trigger the autoimmune response that leads to the development of rheumatoid arthritis in genetically susceptible individuals.
- Obesity: Being overweight can increase the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis and worsen the severity of symptoms in those who already have it .
Diagnosing arthritis begins with a medical examination, in which your doctor looks for signs of inflammation in the joints. This includes checking for swelling, redness, warmth, and tenderness in the joints. They will also evaluate joint motion and identify signs of damage or deformity.
As a complementary method, additional tests may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the disease. These tests may include blood and imaging tests, such as ultrasound, x-rays, and MRI.
Arthritis symptoms

There are many types of arthritis, and symptoms will vary greatly depending on the type. The symptoms can manifest gradually over time or acutely in less frequent cases.
Arthritis typically affects the joints, and in more advanced stages, it can involve organs such as the heart, lungs, and eyes. Some of the typical symptoms include:
- Morning stiffness: The feeling of stiffness and difficulty moving the joints in the morning can usually last more than half an hour in rheumatoid arthritis, while in osteoarthritis, it lasts up to 30 minutes. The most affected joints are usually the hands and wrist, although it can occur in ankles and knees less frequently (4).
- Joint pain: Discomfort and pain in the affected joints may worsen with movement and affect quality of life.
- Swelling and warmth: The affected joints swell, feel warm to the touch, and may have redness due to inflammation.
- Fatigue: A feeling of extreme tiredness that affects both body and mind.
- Loss of appetite
- Malaise: This is a feeling of discomfort in the body, which may include fever.
- Joint deformity: Over time, affected joints may become deformed due to joint degradation, which further hinders movement and causes both aesthetic and functional discomfort.
Symptoms vary from person to person. It depends on the location, age, severity of the disease, and previous medical conditions of the patient.
Can arthritis improve?
When we talk about arthritis, symptoms can improve with proper diagnosis and treatment, depending on the cause .
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease and, currently, there isn’t a curative treatment. However, there are multiple treatments that stop the progression of the disease and keep it inactive, thus avoiding the sequelae of persistent inflammation.
Treating rheumatoid arthritis includes general (non-drug) measures and pharmacological treatment.
What’s good for arthritis and joint pain?
The symptoms of RA usually improve and ease with proper treatment. However, you can make some lifestyle modifications to improve your quality of life and reduce pain (5):
- Avoid stress and engage in healthy physical activity every day. Avoid work that requires repetitive movements, especially of the hands.
- In household tasks, avoid exerting force with the hands. Avoid twisting clothes, opening screw caps, and pressing hard on cutlery handles.
- Maintain an upright sitting position and avoid the neck or back bending for longer periods.
- Sleep an average of 8 to 10 hours at night and take a 30-minute nap. The mattress should be hard, and the pillow should be low. Do not place pillows below the knees.
- Start the day with a hot bath, which will reduce morning stiffness.
Diet
For adequate control of pain, worsening of the symptoms, and complications, follow a varied diet to meet daily requirements.
Scientific evidence shows that food plays an important role in preventing inflammatory diseases (6).
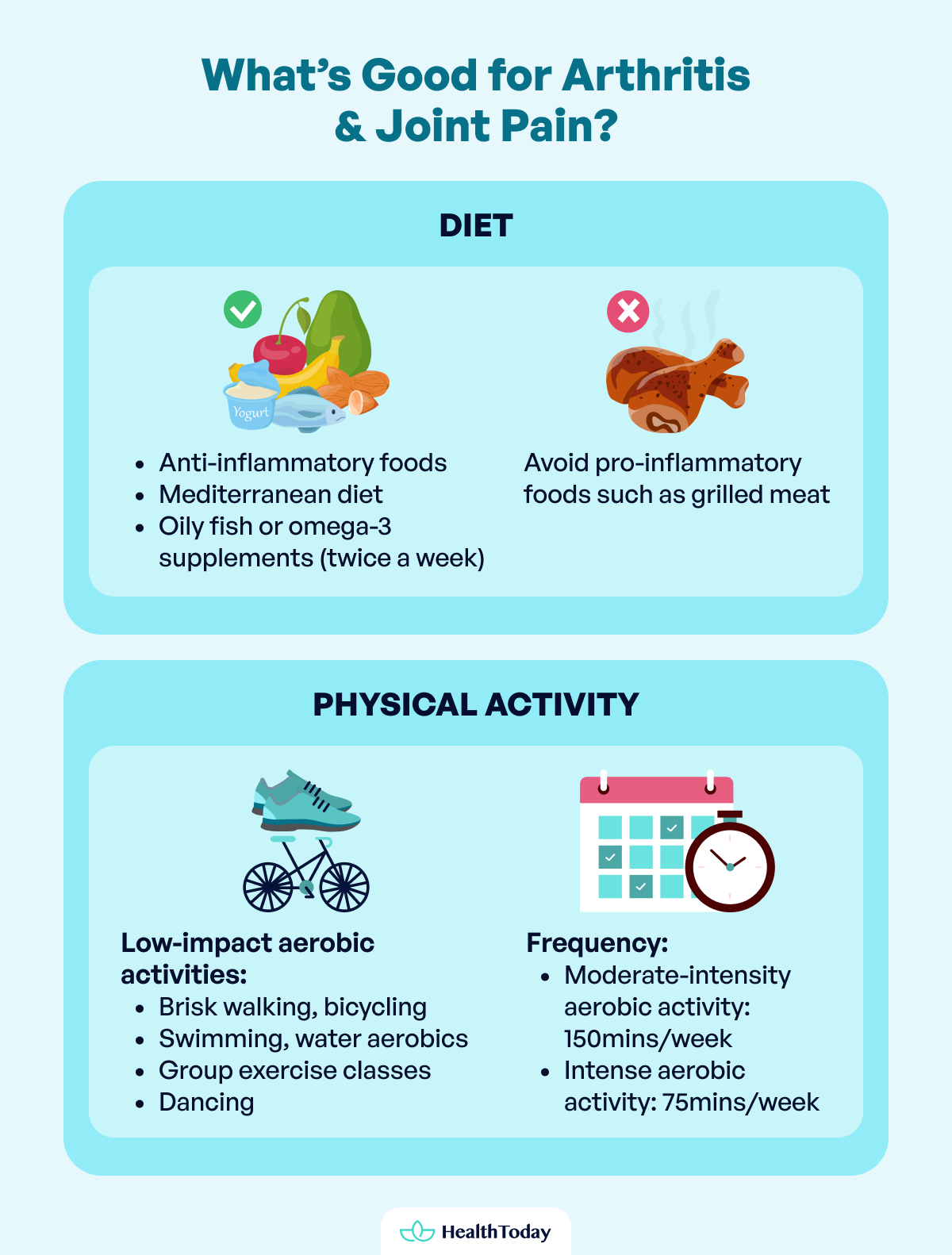
For rheumatoid arthritis, alongside medical treatment, it’s recommended to follow an anti-inflammatory Mediterranean diet (MD) and eat oily fish or omega-3 supplements at least twice a week (6).
The Mediterranean diet is a dietary pattern widely used in the countries surrounding the Mediterranean Sea, such as Greece, Italy, Spain, and parts of France and North Africa. The foods of this diet that you should not miss are:
- Fresh and seasonal foods: The Mediterranean diet is based on the consumption of fresh and seasonal fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds. These foods are rich in vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants, providing a wide range of nutrients essential for health.
- Olive oil: Extra virgin olive oil is used as the primary source of fat in cooking. It is rich in monounsaturated fatty acids and antioxidants. Besides that, it has been associated with various health benefits, such as reducing inflammation and lowering the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Fish and seafood: Regular consumption of fish, especially oily fish such as salmon, sardines, and tuna, is an important feature of this diet. Fish is an excellent source of high-quality protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and other essential nutrients.
- Red wine: Red wine, consumed in moderation, is considered an integral part of the Mediterranean diet, especially during meals.
When it comes to foods that can worsen inflammation and thus worsen arthritis symptoms, grilled meat is a major concern. This form of cooking generates advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs).
These compounds are responsible for triggering inflammatory responses in the body, contribute to the development of autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, and increase the risk of chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and cancer (7).
In summary, eating a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as flaxseed, fruits, and extra virgin olive oil while avoiding pro-inflammatory foods can help reduce inflammation and improve arthritis symptoms.

Physical activity for arthritis
Low-impact aerobic activities are excellent for staying active without putting extra stress on joints. These activities include brisk walking, bicycling, swimming, water aerobics, group exercise classes, and dancing (8).
To obtain significant health benefits, it is recommended to perform at least:
- 150 minutes (2 hours and 30 minutes) of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, such as walking at a brisk pace, cycling at a gentle speed, etc.
- 75 minutes (1 hour and 15 minutes) of intense aerobic activity per week, such as cycling at a higher speed. This type of activity is recommended for patients who have been training for some time.
In addition to aerobic activity, it is crucial to include muscle-strengthening exercises in your routine. You can do weight-lifting exercises, work with resistance bands, or practice yoga to strengthen muscles. These exercises help strengthen all major muscle groups and you can do them two or more days a week.
Exercises are also needed to improve joint function and reduce the stiffness of arthritis. Activities such as yoga or stretching improve flexibility and stability, two important features for older adults to prevent falls and, therefore, fractures.
Treatments and home remedies for arthritis pain relief
Multiple remedies and home treatments help relieve joint pain and improve joint function. We know these diseases have a chronic character. Therefore, the remedies aim to alleviate the worsening symptoms. The most used home remedies are:
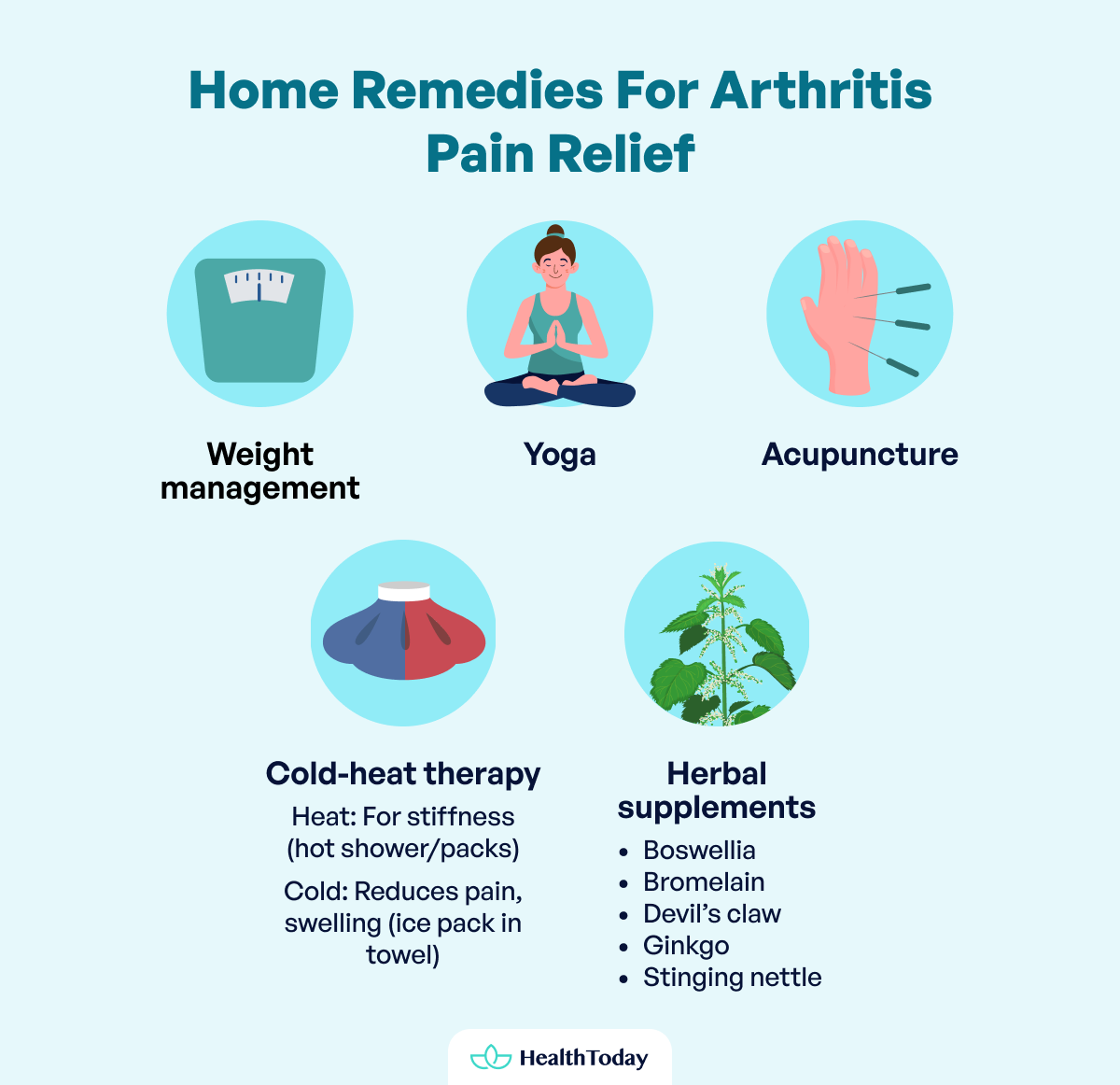

Weight management
Weight reduction is critical as a pain preventive measure, especially in the case of knee arthritis. Being overweight places significant overstress on already inflamed and deteriorated joints, which can result in further damage and pain.
Losing weight not only relieves the burden on affected joints but can also reduce inflammation and improve mobility, thus contributing to a better quality of life.
Research suggests that weight loss can significantly impact knee arthritis symptoms. One study showed that those who lost at least 20 percent of their body weight experienced a considerable reduction in pain and inflammation compared to those who lost only 5 percent (9).
Yoga
Yoga is a practice that combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation. It has been shown to help improve flexibility, muscle strength, and posture while reducing joint stress and promoting relaxation.
In the case of arthritis, certain yoga postures can help relieve stiffness, improve joint mobility, and reduce pain (10). Yoga can also improve sleep quality and overall sense of well-being.
It is adapting yoga postures to individual needs and avoiding movements that may cause pain or additional stress on the affected joints.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is an ancient Chinese medical treatment that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on your body.
Some research suggests that it can help relieve osteoarthritis pain and improve quality of life and physical function, but more research is needed for rheumatoid arthritis (11, 12, 13).
The risk of harm with acupuncture is considerably low. However, more research is needed to fully support its benefits for treating arthritis.
Make sure to find a licensed and certified acupuncturist to perform this treatment.
Cold-heat therapy
Thermotherapy is a commonly used method in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
Heat treatments in the morning may improve joint stiffness in some patients. A hot shower or placing hot packs over joints may be an option.
Cold treatments may help relieve joint pain, swelling, and inflammation. Wrap an ice gel pack in a towel and apply it to painful joints for quick relief. Never apply ice directly to the skin.
Herbal supplements
Several herbal supplements have traditionally been used to help relieve the symptoms of arthritis. However, the scientific evidence for the effectiveness of these supplements may be limited and variable. Some research suggests that the following supplements are beneficial for improving joint pain and function (14):
- Boswellia
- Bromelain
- Devil’s claw
- Ginkgo
- Stinging nettle
Herbal supplements should not replace medical treatments prescribed by health professionals. However, they can be used as complementary therapies to help relieve arthritis symptoms.
Before taking any herbal supplement, you should talk to your doctor to make sure it is safe and appropriate for your medical situation.
When to see a doctor
It is essential to consult a physician if you experience any of the following symptoms related to arthritis:
- Persistent joint pain
- Joint swelling or inflammation
- Extended morning stiffness
- Difficulty in performing daily activities
- Joint deformities
- Joint pain and fever
In summary, if you experience persistent or worrisome arthritis-related symptoms, you must consult a physician to obtain a proper diagnosis and receive the treatment and care necessary to manage the disease.



What can cure arthritis?
Currently, there is no definitive cure for arthritis. However, there are numerous treatments available that can help control symptoms, reduce pain, and improve the quality of life for people living with this condition.
These treatments may include medications, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, regular exercise, and, in some cases, surgery.
Can you get arthritis in your twenties?
Although arthritis is more common in older people, certain types, such as juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis, can affect people of all ages, even in their twenties.
Can you live with arthritis without treatment?
While it is possible to live with arthritis without treatment, it is not recommended. Arthritis is a chronic, progressive disease that can cause irreversible joint damage if not properly treated. Treatment can help control symptoms, prevent joint deterioration, and improve quality of life.
What is the most effective treatment for arthritis?
The most effective treatment for arthritis may vary depending on the specific type of arthritis and the severity of the disease.
Can too much walking make arthritis worse?
In general, regular exercise, including walking, is beneficial for people with arthritis, as it can help strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce joint stiffness.
It is advisable to consult with a physician or physical therapist to determine the appropriate amount of exercise for your situation.
Summary
Arthritis is a condition that affects people of all ages and is characterized by inflammation of the joints. There are different types of arthritis, two of the most common being osteoarthritis and inflammatory arthritis like rheumatoid arthritis.
Osteoarthritis, the most common form of arthritis, occurs due to the wear and tear of cartilage in the joints. It can cause pain, stiffness, and loss of motion in the affected joints and usually develops over time due to aging and normal joint wear and tear.
Conversely, inflammatory arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, results from an overactive immune system attacking the joints themselves, causing chronic inflammation. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most common types of inflammatory arthritis and can cause pain, swelling, stiffness, and deformities in the joints.
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis may include joint pain, swelling, stiffness, fatigue, joint deformities, loss of appetite, low-grade fever, and extended morning stiffness.
It is important to pay attention to the warning signs of arthritis, which may include persistent joint pain, significant swelling, prolonged morning stiffness, difficulty performing daily activities, joint deformities, and systemic symptoms such as fatigue, fever, or weight loss.
While there is no cure for arthritis, home treatments, such as heat and cold therapy, regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, herbal supplements, and adequate rest, can help relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.

















Comments
0